- What Does “High Circuit Breaker Voltage” Mean?
- Applications of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
- Market Trends and Global Evolution
- Technical Specifications: What Defines “High Voltage”?
- Types of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
- High-Voltage vs Medium-/Low-Voltage Breakers
- Selection Criteria: How to Choose the Right Breaker?
- Top Manufacturers of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
- Frequently Asked Questions
When discussing modern power systems, one critical component that stands out is the high-voltage circuit breaker. These devices are the guardians of grid stability, ensuring that faults and overloads are safely interrupted before damage spreads through transmission networks. In this article, we delve into the meaning of high circuit breaker voltage, its applications, technical parameters, and guidance for selecting the right equipment—while aligning with Google SEO best practices and reinforcing EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) principles.
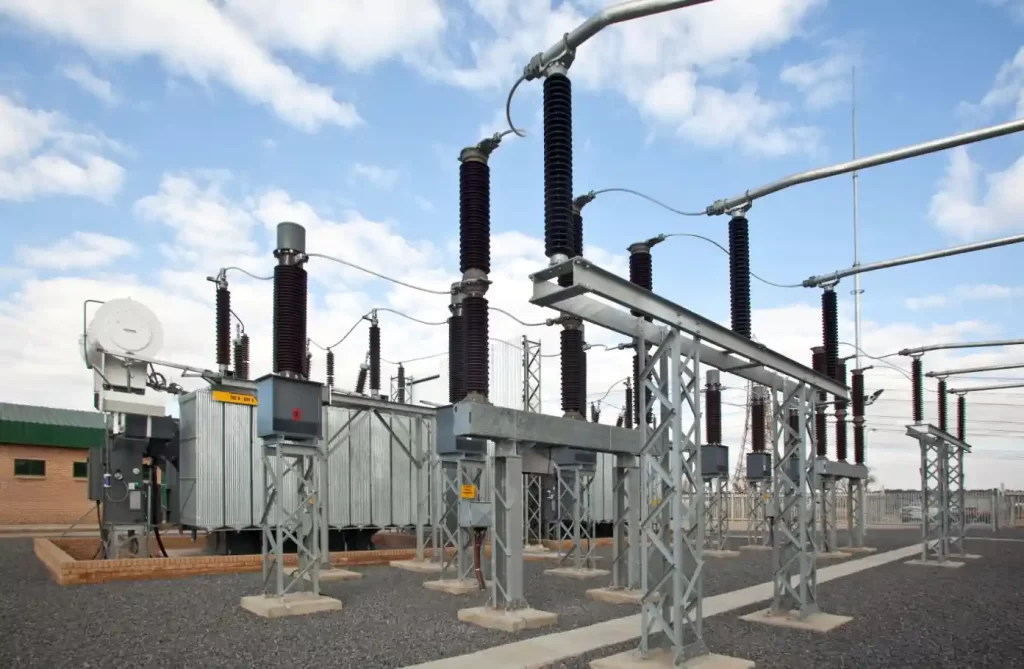

What Does “High Circuit Breaker Voltage” Mean?
High circuit breaker voltage refers to the maximum system voltage a circuit breaker is designed to interrupt safely. In high-voltage applications, this typically means voltages above 36kV, often in the range of 72.5kV, 132kV, 245kV, 400kV, and even up to 800kV for ultra-high-voltage systems.
These breakers are engineered to manage enormous energy levels and must function with millisecond precision, making their design and testing far more complex than their low-voltage counterparts.
Applications of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
High-voltage circuit breakers are essential in the following domains:
- Transmission Substations (e.g., 132kV and 400kV levels)
- Power Generation Plants
- HVDC Converter Stations
- Renewable Energy Integration (e.g., large-scale solar/wind farms)
- Industrial Facilities with HV equipment
- Railway Electrification Systems
Their primary function is to detect faults and interrupt current flow without endangering equipment, personnel, or system stability.

Market Trends and Global Evolution
The global high-voltage switchgear market, including circuit breakers, is experiencing robust growth. According to IEEMA and the International Energy Agency (IEA), the demand for high-voltage protection equipment is being driven by:
- Grid modernization and expansion
- Renewable energy integration
- Urbanization and industrialization
- Need for higher energy efficiency and resilience
Moreover, manufacturers are moving toward SF₆-free technologies in response to environmental concerns, as traditional breakers often use SF₆ (a potent greenhouse gas) as an insulating medium.
Technical Specifications: What Defines “High Voltage”?
| Specification | Typical Range for HV Circuit Breakers |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 72.5kV – 800kV |
| Rated Short-Circuit Current | 25kA – 63kA |
| Rated Frequency | 50Hz / 60Hz |
| Breaking Time | < 3 cycles (60ms or less) |
| Insulation Medium | SF₆, Air, Vacuum, or Eco-Gas |
| Mounting | Outdoor, GIS, Dead Tank, Live Tank |
| Standards | IEC 62271, IEEE C37.04, ANSI C37.06 |
Types of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
- SF₆ Circuit Breakers
- Use sulfur hexafluoride gas for arc quenching and insulation
- Very common above 72.5kV
- Compact design but environmental concerns apply
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs)
- Rare for HV but emerging in 72.5kV range
- Very low maintenance and eco-friendly
- Air-Blast Circuit Breakers
- Use compressed air to extinguish arcs
- Mostly replaced by SF₆ breakers
- Oil Circuit Breakers
- Historically used, now largely obsolete due to maintenance and safety issues
- Hybrid or Clean-Air Circuit Breakers
- Use environmentally friendly gas mixtures or air
- Growing adoption in Europe (e.g., Siemens Blue GIS technology)
High-Voltage vs Medium-/Low-Voltage Breakers
| Feature | High-Voltage CB | Medium-/Low-Voltage CB |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | > 36kV | ≤ 36kV |
| Arc-Quenching Medium | SF₆ / Vacuum / Air | Mostly Vacuum / Air |
| Use Case | Transmission / Utility Grid | Buildings, Panels, MCCs |
| Installation | Outdoor / Substation | Indoor / Cabinets |
| Complexity | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Selection Criteria: How to Choose the Right Breaker?
When selecting a high-voltage circuit breaker, consider the following:
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Must match or exceed system specifications
- Interrupting Capacity: Evaluate worst-case fault current
- Insulation Type: SF₆ for compactness; Air or Eco-Gas for environmental compliance
- Installation Space: GIS is ideal for urban substations; AIS requires more space
- Maintenance Requirements: Vacuum and sealed designs offer lower O&M
IEEE C37.010 and IEC 62271-100 are excellent starting points for standardized selection.
Top Manufacturers of High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
The global high-voltage switchgear landscape is dominated by:
- ABB (Hitachi Energy) – Known for hybrid and SF₆ breakers up to 800kV
- Siemens Energy – Leader in SF₆-free high-voltage circuit breakers
- GE Grid Solutions – Strong portfolio in live-tank and dead-tank GIS systems
- Schneider Electric – Offers modular, eco-conscious HV systems
- Mitsubishi Electric – Robust dead-tank circuit breakers
- PINEELE – Emerging provider with cost-effective HV breaker lines for 72.5kV–145kV grids
Frequently Asked Questions
A: Anything above 36kV is generally classified as high voltage. Typical high-voltage breakers handle 72.5kV, 132kV, 245kV, 400kV, or higher.
A: SF₆ is an excellent insulator and arc quencher, allowing compact, safe, and efficient operation—though its environmental impact has prompted a shift toward greener alternatives.
A: While vacuum breakers dominate the medium-voltage segment, some designs are now available for up to 72.5kV, though they are less common above that threshold.
High circuit breaker voltage is more than just a technical specification—it defines the capability of a system to protect, isolate, and operate safely under extreme electrical stress. Understanding voltage levels, arc quenching methods, and breaker technologies empowers engineers and facility managers to make informed, future-proof decisions.
As power systems evolve toward higher capacities and greener technologies, choosing the right high-voltage circuit Breaker becomes a strategic investment in both safety and sustainability. Always refer to international standards, consult trusted manufacturers, and ensure your equipment aligns with operational and environmental requirements.
